Copyright 2020 by Gary L. Pullman
10 Andrew Swofford
Apparently, some spirits of
the dead are transvestites. Perhaps too embarrassed to buy clothes of their own
(or too poor—most ghosts, it seems, have little or no need, as a rule, for
cash, checks, credit cards, or bank accounts), one apparition decided to raid
the closet Maddie, of a University of North Carolina at Greensboro.
Maddie and her roommates live
off-campus, in the Edge Apartments on Oakland Avenue, but it was Maddie whose
shirts and pants went missing. The ghost proved more tangible than most,
leaving its handprints on the apartment's bathroom wall.
When she heard “rattling” in
her closet on February 4, 2019, Maddie went to investigate, thinking maybe a
raccoon had been trapped inside. That's when she caught the ghost red-handed
(so to speak). He was wearing her socks and shoes and had heisted a bag of her
clothes. He tried on one of Maddie's hats, before inspecting himself in her
bathroom mirror and, after complimenting her appearance, asked for a hug, but
never touched her.
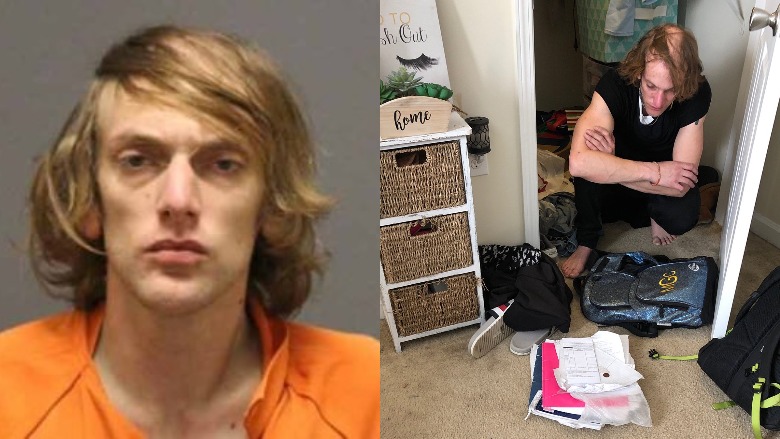
The ghost turned out to be
30-year-old Andrew Swofford. He was
arrested on fourteen felony counts, including larceny and identity theft, and
held on a $26,000 bond. Maddie and her roomies have since moved out of the
apartment, having found their flesh-and-blood intruder more unnerving than the
ghost they'd believed was haunting their abode.
9 Krushna Chandra Nayak
In August, 2018,
forty-five-year-old Nakula Nayak and his brother Shyam Nayak, both of whom
lived out of town, in Chhelianala, India, came to the village of Angikala to
notify a relative, Sahadev Nayak, that their mother had died. Due to the
lateness of the hour, the brothers stayed overnight with Sahadev.
Around midnight, Nakula went
outside, to a field close by, to relieve himself. Coincidentally, Sahadev's
cousin, Krushna Nayak, was working outdoors. The night was quite dark, and when
Krushna saw Nakula, Krushna mistook the
visitor for a ghost.
Terrified, Krushna began
beating Nakula with a lathi, a heavy, iron-bound bamboo stick. During the
struggle, Nakula managed to wrest the weapon from Krushna and began to strike
his assailant, believing his attacker to be a ghost, just as Krushna had
mistaken Nakula for a spirit. Nakula's assault on Krushna proved fatal, and
Nakula was arrested by the Turumunga police after Krushna's family lodged a
complaint against him.
8 Unidentified Helena,
Montana, Man
Was the shooter's reason for
shooting at a 27-year-old Helena man nothing more than a lame excuse, or did
the gunman really believe that his quarry, who was setting up targets on public
land, a Bigfoot?
The victim told police bullets
came flying at him, left and right, as he positioned the targets. When additional
rounds were fired at him, he sought cover among trees. Later, he emerged to
“confront” the shooter, who drove a black Ford F-150 full-size pickup truck.
The Helena man said the man
who targeted him in December, 2018, had mistaken him for Bigfoot. “I don’t
target practice,” he explained, “but if I see something that looks like
Bigfoot, I just shoot at it.” To prevent others from making a similar mistake,
the shooter suggested that his victim wear an orange vest.
Initially, police were
skeptical of the man's report, because he was unable to describe the alleged
shooter, did not want to file charges, and was reluctant to speak to deputies.
Authorities were unable to locate a truck in the area that fit the description
of the Ford F-150 pickup.
Then, a woman reported a
similar incident involving a man who drove a vehicle of the same color, make,
and model and had shot at her. She was able to provide a solid description of
her assailant.
“We’re working to find this
person,” Lewis and Clark County Sheriff Leo Dutton said. “It is of great
concern that this individual might think it’s okay to shoot at anything he
thinks is Bigfoot.” If apprehended, the shooter could be charged with attempted
negligent homicide.
7 Wendy
Thinnamay Masuka
In April, 2018,
thirty-seven-year-old Zimbabwe pastor Masimba Chirayi killed Wendy Thinnamay Masuka while baptizing her. The adult
congregant had reacted violently to the baptism, he said.
Her
violence indicated to him that she was a “vampire possessed by demons,” and he
believed that she might “kill people.” To prevent this possibility, Chirayi
deliberately “kept her submerged in water until [he] overpowered her.”
Following
his appearance in a magistrate's court in Zimbabwe, the pastor was granted
bail.
6 Helaria Montepon Gumilid
Mistaking Helaria Montepon
Gumilid, a 79-year-old widow, for an aswang (a carnivorous shape-shifter that
may appear to be an ordinary person, despite “reclusive habits or magical
abilities,” Helaria's daughter-in-law, Myrna Damason Gumilid, age 49,
and Myrna's two sons, Rene Boy Gumilid, age 28, and Joseph Damason Gumilid, age
23, hacked her to death.
In April, 2014, the victim had
been visiting her mentally-ill grandson in Zamboanga City, Philippines, when
she was attacked and killed. Myrna, Rene
Boy, and Joseph bound Helaria, “slit her armpits,” hacked her to death, and
removed one of her organs to prevent her from “regenerating.”
Authorities arrested the
suspects, whom they planned to charge in the horrific crime.
5 African Man
In October, 2010, firefighters
responding to a report that people had jumped from the third-story balcony of a
housing unit in the village of La Verriere, France, discovered seriously
injured relatives among the eleven family members who'd made the leap. They
also found a two-year-old survivor, a baby, and a nude African man with a knife
wound to his hand. The baby later died at a hospital in Paris. (La Verriere is
located on the edge of the city.)
Thirteen people were watching television
in the apartment when the naked man, hearing the baby cry, rose to prepare a
bottle for the child. His wife screamed, “It's the devil! It's the devil!” His
sister-in-law stabbed him in the hand, and he was thrown out of the apartment.
When he tried to return, the
others panicked, leaping from through the window, one man with the two-year-old
girl in his arms. The man crawled away, hiding in bushes tow blocks away. “I
had to defend myself,” he screamed. Seven of the jumpers required medical treatment
for multiple injuries.
No hallucinogenics and no
indication of the practice of any occult rituals were found. The assistant
prosecutor from Versailles, Odile Faivre, admitted, “A number of points remain
to be cleared up.”
4 James Velasco
Hacked, bitten, and beaten,
James Velasco was killed by his grandfather, Orak Mantawil, during a December,
2015, power outage at their family-owned residence in Bliss, Barangay Nituran,
Parang, Maguindanao.
Mantawil was carrying his
four-year-old grandson in his arms when he mistook James for a tiyana, a
vampire who assumes the form of a child or a newborn infant. He apologized to
his family and the boy's parents, saying that he was drunk and cannot recall
what happened after he saw James as a tiyana. He told investigators that he
does not “use drugs.”
James's parents brought
charges of parricide against Mantawil. “He could no longer bring back my
child’s life even though he asked forgiveness,” said Fatima Velasco, James's
mother and Mantawil's daughter. She also said, “My child sustained human bites.
It appeared like his blood was sucked.”
Mantawil has been arrested and
will be subjected to a psychological examination and a drug test.
3 Stella
After Stella was caught
tiptoeing on graves at Luveve Cemetery in Bulawayo,
Zimbabwe, in 2018, a crowd meted out vigilante justice, beating the woman, who
they regarded as a witch searching for corpses she could cannibalize.
A
Luveve resident said, “I was on my way to work when I saw a woman with torn,
dirty clothes talking to herself while tiptoeing on the graves. I quickly
called out to other people passing by.” When asked her name, the woman
repeatedly replied “Stella.”
The
crowd set upon her, whipping her until she wailed in pain. Police rescued her
when they arrived on the scene, and Stella was taken to the police station,
where, Bulawayo police spokesperson Inspector Abednico Ncube said, she was
found to be “mentally unstable” and to be guilty of nothing more than of having
been “at the wrong place at the wrong time.” A family who'd reported the woman
missing identified her as a relative.
2 Zana
Bryan Sykes, professor of
human genetics at the University of Oxford, said a West African DNA strain
might belong to a human subspecies.
The DNA sample was taken from
a hirsute, auburn-haired, 6'6”-tall, mid-19-century African slave named Zana
who lived in mid-19th-century Russia proves she was 100-percent African,
despite the fact that she didn't look like any modern African group of people.
In fact, according to a
Russian zoologist, “her expression . . . was pure animal.”
Sykes suggests that she and
her ancestors left Africa 100,000 years ago to dwell in the region of the
Caucasus Mountains. His most astonishing claim, however, is that Zana might
have been a yeti, or so-called abominable snowman.
Several critics are more than
a bit skeptical of Sykes's claims. For example, Jason Colavito points out that,
by Sykes's own admission, the geneticist “has found no genetic evidence that
yet points conclusively to a pre-modern origin for Zana” and suggests that the
characterization of her as being more “animal” than human might have a racist
origin: “As best I can tell, there are no nineteenth century primary sources
related to Zana, and all of the accounts of her large, apelike appearance
derive from local lore recorded more than a hundred years after the fact, and
during a time when Black Africans were routinely described as apelike,
particularly by isolated rural populations with little or no contact with other
races.”
It seems possible that Sykes
has mistaken Zana for a yeti, when, in fact, she was actually a 19th-century
African slave.
1 Horseman (Centaur)
Ancient people also sometimes
mistook people for imaginary creatures.
Imagine the shock that ancient
Greeks and other Mediterranean peoples experienced when they first witnessed
mounted Eurasian soldiers invading their lands. The cavalry was unknown to
them. The horsemen must have seemed a perfect union of man and horse, a hybrid
fusion of the human and the equine. Such warriors would have been terrifying,
and warriors wielding shields and striking with swords must have seemed
invincible.
As Bjarke Rink observes in his
book, The Rise of the Centaurs, “The impact of cavalry action upon
farming societies was shattering”—and this sight was the origin of the mythical
creature known as the centaur, a presumed hybrid of man and beast that the
ancient Greeks mistook for true monsters: “The weird creature that captured the
world's imagination for thousands of years was not a myth at all, but the first
sighting of fighting horsemen by the peasant farmers of Greece.”






.jpg/1024px-Leopard_(Panthera_pardus).jpg)

.jpg/300px-Gunsore_leopard_(Somnapur_village%2C_Seoni_district).jpg)















